FAQ
If you would like to book an appointment or get additional information about our clinic, please fill our form on the contact page or contact us directly by phone at (604) 282-1284. We promise not to disclose your information to any third parties. For Appointment bookings, please specify your preferred dates and time in the comment box and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
Thank you.
Table of contents:
- What is Physiotherapy?
- What is Orthopaedic Manual Therapy?
- What is IMS?
- FCAMPT
- My First Visit
- Rates & Cancellation Policy
- ICBC/ WorkSafe BC (WSBC)
- From a legal perspective
What is Physiotherapy?
 Physiotherapy is a branch of medicine dedicated to the treatment of muscle, joint, bone and nerve related injury and dysfunction. It is the primary health care profession that works along side medical doctors to promote wellness, mobility, relieve pain and restore function. Physiotherapists are all university trained holding baccalaureates, masters, and doctorate degrees. Their education and clinical training gives them the knowledge and skills to assess and treat illness and injury. Because of their training, they are competent to identify when a client’s symptoms are beyond the physiotherapy scope of practice and will be able to direct the client to the appropriate health care professional.
Physiotherapy is a branch of medicine dedicated to the treatment of muscle, joint, bone and nerve related injury and dysfunction. It is the primary health care profession that works along side medical doctors to promote wellness, mobility, relieve pain and restore function. Physiotherapists are all university trained holding baccalaureates, masters, and doctorate degrees. Their education and clinical training gives them the knowledge and skills to assess and treat illness and injury. Because of their training, they are competent to identify when a client’s symptoms are beyond the physiotherapy scope of practice and will be able to direct the client to the appropriate health care professional.
As primary health care professionals, patients do not need a physician’s referral to see a physiotherapist. Patients covered under MSP, WCB and ICBC for example do not need a physician’s referral for physiotherapy. Most extended health care plans also recognize the need for direct access as well, however, a few still require a physician’s referral for reimbursement purposes.
On your first visit you can expect that your physiotherapist will take a thorough medical history and ask you questions about your areas of complaint, how the injury occurred, and anything else that would be relevant including work conditions, exercise habits, overall health, previous injuries, family history, etc. Your physiotherapist will be able to take a look at the big picture from past to present and narrow the focus to better explain why you are having the pain and dysfunction you are having now. Physical examination and testing follows the history taking and is a critical component of the initial evaluation process as it confirms the diagnosis and identifies which tissues (muscle, cartilage, bone, nerve) are involved and to what extent they are injured. This is very important and must be done correctly because different tissues need to also be treated very differently. Accurately identifying which tissues are injured the first time means a faster recovery for you.
A trained manual physical therapist will be able to palpate and identify whether a joint is restricted, hypermobile, in spasm, arthritic, or bound down by scar tissue. It is this part of the physical assessment that requires the most amount of training and experience since a joint restriction is treated entirely different from a hypermobile joint or segment. The prescription of medical exercises following manual therapeutic intervention is vastly different in a joint restriction as compared to an unstable joint. For instance, in the unstable joint, exercises must work to enhance joint stability and limit the overall range of motion and enhance joint control, where as in the restricted joint, exercises must challenge the end ranges of motion and it may be necessary to hold the joint in certain angles to promote a stretch of the joint capsule. Once again, manual diagnostic techniques are crucial in determining the appropriate exercises and promote faster recovery.
What is Orthopaedic Manual Therapy?
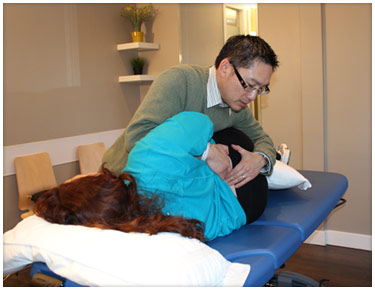 ORTHOPAEDIC MANUAL THERAPY (OMT) OMT has it’s roots in medicine dating back to 400 BC when Hippocrates first used manual techniques to alleviate low back pain. Although medicine and manual therapy has evolved and advanced very much since then, Hippocrates, also known as the “father of medicine”, can be credited for laying the foundation upon which manual physiotherapists practice even today.
ORTHOPAEDIC MANUAL THERAPY (OMT) OMT has it’s roots in medicine dating back to 400 BC when Hippocrates first used manual techniques to alleviate low back pain. Although medicine and manual therapy has evolved and advanced very much since then, Hippocrates, also known as the “father of medicine”, can be credited for laying the foundation upon which manual physiotherapists practice even today.
OMT is a specialized branch of physical medicine requiring advanced level of physical therapy training where skilled specific hands-on techniques such as manipulation/mobilization are used for the management of neuro-musculo-skeletal conditions. Scientific medical exercise and manual methods are based on clinical reasoning, evidence, and a thorough understanding of anatomy and physiology, and underpins all effective treatment plans. Expected outcomes may include managing pain, increasing range of motion, reducing soft tissue tension, eliminating joint inflammation, increasing joint mobility, improving joint stability, restoring normal movement patterns, improving general fitness, and returning to work, sport, and daily activities.
OMT is employed by physiotherapists and physicians alike in the diagnosis and treatment of impaired soft tissues and joint structures. Manual therapy diagnostic techniques form the medical justification for ordering radiological tests such as MRIs and CT Scans. Manual therapy treatment techniques modulate pain, increase range of motion, reduce or eliminate soft tissue inflammation, induce relaxation, improve contractile and non-contractile tissue repair, extensibility and/or stability, facilitate movement and improve function.
For more on the history of OMT:
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2565620/pdf/jmmt0015-0165.pdf
What is IMS?
Intramuscular Stimulation (IMS) is a dry needling technique that uses acupuncture needles to release shortened and tender muscle bands from neuro-musculoskeletal dysfunction. It is a diagnostic and treatment tool for myofascial pain of neuropathic origins. This treatment technique was first developed by Dr. Chan Gunn (C.M., O.B.C., M.D., PhD.), and bridges the gap between traditional Chinese acupuncture and western medicine.
How does IMS work?
Very often, the nerves throughout your body can get hypersensitive, stemming from trauma and/or repetitive strain. When irritated, nerves’ supply to your muscles becomes abnormal, which in turn causes the muscles to become super-reactive and shortened. This manifests itself as tightness and stiffness in your body. After a fine needle is inserted into a supersensitive muscle, the muscle will grasp it and create a cramping sensation. This will then stimulate a reaction that leads to the release of endorphins, resulting in relaxation. The tiny wound caused by the needle’s introduction into the muscle can further induce the healing process. Once the tension in your muscle has been reduced, it decreases stress and tendon slackening, and decreases the pressure that is being put on your joints, discs, and nerves. As a result, the pain signal is reduced and the muscle relaxation slowly returns the blood flow to the area. Furthermore, this allows the nerve and muscle to re-pattern to normal function. A diagnostic test such as an X-ray, CT scan, or MRI may not show any visible signs of your injury, making it impossible to detect supersensitive muscles through conventional means. However, an assessment by a trained Gunn IMS practitioner can help determine if this technique is suitable for you.
What conditions may benefit from IMS?
A wide range of neuro-musculoskeletal problems, such as the following:
- Tension and headaches
- Neck pain and whiplash
- Upper, mid, and low back pain
- Frozen shoulder and rotator cuff tendonopathy
- Tennis elbow
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Sciatica/piriformis syndrome
- Leg stiffness/numbness
- Plantar fasciitis
- Repetitive strain injuries
Does IMS hurt?
When a needle is inserted into a normal muscle, you will only feel the prick of the needle itself. However, if you have supersensitive muscles, you will feel a cramping, aching, or even grasping sensation. Some patients describe it simply as a pressure point, and some patients describe it as akin to a Charlie Horse. After your IMS treatment, you may experience increased soreness for a few days, followed by improvement in your overall pain state. Mild heat and resting may help to relieve post-treatment soreness.
How often is IMS needed?
Typically, treatments are once every 1-2 weeks in order to allow time for your body to recover. The number of treatments depends on the severity of the problem, the nature of the condition, your general health, your body’s healing ability, and the condition of your nerves. According to a published study on low back pain, the average number of treatments is 8.2 sessions.
What should I wear to my appointment?
Wear something that allows your physiotherapist to access the area of concern in order to perform a full examination of the spine and limbs, i.e., shorts and a bra instead of a tank top. Gowns are available if needed.
Who can practice IMS?
IMS is practiced in British Columbia by Certified Gunn IMS Practitioners (CGIMS), who are either registered physiotherapists or medical doctors. Currently, UBC Gunn IMS training operates under the British Columbia College of Physicians and Surgeons and the BC College of Physical Therapists.
How can I access IMS treatment?
If you think you have a condition that may benefit from IMS, you can simply make an appointment with our Gunn IMS qualified physiotherapists, Agnes Ku, BScPT (Hons), BScKin, UBC CGIMS and Jonathan Lui, MScPT, HBSc, CAFCI. IMS is included in the scope of physiotherapy practice. Our physiotherapists will assess your condition and advise you on the best approach for it. For further detailed information, please browse the following websites: http://ubcgunnims.com http://istop.org
FCAMPT
The Canadian Academy of Manipulative Physiotherapy (CAMPT) is Canada’s member organization of the International Federation of Manipulative Physical Therapists (IFOMPT) which is part of the World Confederation of Physical Therapy and the World Health Organization. CAMPT’s role is to advance orthopaedic manual therapy practice, education and research in Canada, and to monitor Canadian education programs to ensure they continue to meet the standards of IFOMPT. Our members are all physiotherapists, who have chosen to focus their skills in the area of orthopaedics (muscle, nerve and joint problems). We treat our patients using manual therapy and specifically tailored exercise programs.
“Fellow” status in the CAMPT is both a membership classification and a professional credential. As a professional credential, a “Fellow” in CAMPT is an international recognition of competence and expertise in the practice of orthopaedic manual therapy by a physiotherapist licensed in the Canada. To achieve the Fellow credential, a physiotherapist must complete a credentialed fellowship program in manual therapy. The “Fellow” is a physiotherapist who has demonstrated advanced clinical, analytical, and hands-on skills in the treatment of neuro-musculo-skeletal disorders. Fellows serve their patients and the public by demonstrating excellence in clinical practice, education, and research.
To maintain the professional credential of Fellow, a physiotherapist must be a member in good standing in the CAMPT. The Fellow membership classification affords the member special privileges to vote on issues related to practice standards, international affairs, and bylaw changes. Additionally, only Fellows are allowed to serve on the executive committee as President, Vice-President, Secretary, or Treasurer (any member in good standing may serve on the executive committee as Member-at-Large). These requirements are in place to comply with the constitution and bylaws of the International Federation of Manipulative Therapist (IFOMPT) of which the CAMPT is the representative organization from the Canada.
Credentials Acronym Definitions:
FAAOMPT – Fellow of the American Academy of Manipulative Physiotherapy
FCAMPT – Fellow of Canadian Academy of Manipulative Physiotherapy
CAFCI – Certificate of the Acupuncture Foundation of Canada Institute
DPT – Doctorate of Physical Therapy
MPT – Masters of Physical Therapy
BScPT – Bachelors of Physical Therapy
BScKIN – Bachelor’s of Science in Kinesiology
MTC – Manual Therapy Certificate
MCPA – Member of the Canadian Physiotherapy Association
IMS – Intramuscular Stimulation
My First Visit
Please come in 10-15minutes prior to your first appointment so you can fill out some paperwork without cutting into your appointment time. You can also choose to download the forms directly below, under Patient Intake/Consent Form, and bring it into our clinic at the time of your appointment.
Please wear comfortable clothing for your treatments:
For example:
- Tank tops/t-shirts: upper body injuries that require revealing certain areas of the body
- Shorts: for hip, knee and low back injuries
- We also have shorts and gowns for those who didn’t have time to prepare
Our Rates
For full details and Fee Schedule, please call us at (604) 282-1284
Cancellation Policy
Your appointment time is reserved specifically for you. If you need to reschedule an appointment, 24hrs notice is required so we may give this time to someone else, otherwise a cancellation fee will apply for the time lost. Thank you for your cooperation.
